Are you Ready? Ready to go beyond the hype and actually build with AI? This book is your complete hands-on guide to creating text generators, image transformers, voice models, chatbots, and more — all using open-source tools, local models, and step-by-step instructions.
Perfect for learners, makers, and engineers, this project-based guide walks you from the basics of running a simple language model on your laptop to advanced fine-tuning, multimodal workflows, and real deployment techniques.
Every chapter is a self-contained project — complete with Python code, environment setup, and friendly guidance to help you get it running, even if it's your first time touching machine learning.
The following gives you an overview of the chapters - also some insights of the code and expected generated results.
Create your first local text generation project using GPT-2, perfect for beginners learning AI text generation.
textgpt-2beginnerResources
-
# conda env create -f environment.yml
# conda activate gpt2-local
# conda deactivate
# conda env remove --name gpt2-local
name: gpt2-local
channels:
- defaults
- conda-forge
dependencies:
- python=3.9
- pip
- pip:
- transformers==4.28.1
- torch>=1.12.0
- colorama>=0.4.6
- numpy<2.0.0
- pandas
-
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd # need panda package
import torch
import sys
print("Environment ready!")
print("Python version:", sys.version)
print("NumPy version:", np.__version__)
print("Pandas version:", pd.__version__)
print("PyTorch version:", torch.__version__)
# Check CUDA availability and version
if torch.cuda.is_available():
print("CUDA is available.")
print("CUDA device count:", torch.cuda.device_count())
print("Current device:", torch.cuda.current_device())
print("Device name:", torch.cuda.get_device_name(torch.cuda.current_device()))
print("CUDA version:", torch.version.cuda)
else:
print("CUDA is NOT available.")
from transformers import pipeline
generator = pipeline("text-generation", model="gpt2")
prompt = "Once upon a time in a distant galaxy,"
result = generator(prompt, max_length=50, num_return_sequences=1)
print(result[0]['generated_text'])
Build an automatic prompt completion tool using the GPT-Neo model.
textgpt-neopromptsResources
-
# conda env create -f environment.yml
# conda activate gpt-neo-local
# conda deactivate
# conda env remove --name gpt-neo-local
name: gpt-neo-local
channels:
- defaults
- conda-forge
dependencies:
- python=3.9
- pip
- pip:
- transformers>=4.33.0
- torch>=2.0.0
- accelerate>=0.21.0 # for gpu
- numpy<2.0.0,>=1.23.0
- pandas==1.5.3
-
from transformers import pipeline
generator = pipeline("text-generation", model="EleutherAI/gpt-neo-1.3B")
prompt = "The spaceship began to shake violently as"
output = generator(prompt, max_length=100, do_sample=True, temperature=0.9)
print(output[0]['generated_text'])
Create Japanese haiku poems using Markov chains for simple text generation.
textmarkovpoetryResources
-
# conda env create -f environment.yml
# conda activate haiku-markov
# conda deactivate
# conda env remove --name haiku-markov
name: haiku-markov
channels:
- defaults
dependencies:
- python=3.9
- pip
- pip:
- numpy>=1.21.0
- syllables>=1.0.0
- nltk>=3.7
- pyphen==0.14.0
-
# Part 1
print('part 1')
import random
def build_markov_chain(text):
words = text.split()
chain = {}
for i in range(len(words) - 1):
word, next_word = words[i], words[i + 1]
chain.setdefault(word, []).append(next_word)
return chain
def generate_text(chain, length=10):
word = random.choice(list(chain.keys()))
result = [word]
for _ in range(length - 1):
next_words = chain.get(word)
if not next_words:
break
word = random.choice(next_words)
result.append(word)
return ' '.join(result)
sample = "The fox runs through the forest. The forest is quiet and green."
chain = build_markov_chain(sample)
print(generate_text(chain, length=12))
# Part 2
print('part 2');
import pyphen
dic = pyphen.Pyphen(lang='en')
def count_syllables(line):
return sum(len(dic.inserted(word).split('-')) for word in line.split())
def generate_line(chain, target_syllables):
for _ in range(1000): # Try up to 1000 times
text = generate_text(chain, length=10)
if count_syllables(text) == target_syllables:
return text
return "(couldn't generate line)"
def generate_haiku(chain):
return "\n".join([
generate_line(chain, 5),
generate_line(chain, 7),
generate_line(chain, 5),
])
corpus = open("poems.txt").read()
chain = build_markov_chain(corpus)
print(generate_haiku(chain))
-
💡
poems.txt (Download TXT)
(83 bytes)
Generate complete short stories offline using the GPT-J model.
textgpt-jstoryResources
-
# conda env create -f environment.yml
# conda activate gptj-local
# conda deactivate
# conda env remove --name gptj-local
name: gptj-local
channels:
- defaults
- conda-forge
dependencies:
- python=3.9
- pip
- pip:
- torch>=2.0.1
- transformers>=4.31.0
- accelerate>=0.21.0
- bitsandbytes>=0.41.0
- einops>=0.6.1
- numpy<2.0.0
-
# part 1
print('part 1')
import torch
import sys
print("Python:", sys.version)
print("Torch:", torch.__version__)
print("CUDA available:", torch.cuda.is_available())
if torch.cuda.is_available():
print("Device:", torch.cuda.get_device_name(0))
print("VRAM:", round(torch.cuda.get_device_properties(0).total_memory / 1e9, 2), "GB")
else:
print("Running on CPU only.")
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, pipeline
model_id = "EleutherAI/gpt-j-6B"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_id,
torch_dtype=torch.float16 # use less memory
)
generator = pipeline("text-generation", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer, device=0)
# part 2
print('part 2')
prompt = "The airlock hissed open, and Captain Reyes stepped onto the alien soil."
result = generator(prompt, max_length=250, do_sample=True, temperature=0.9)
print(result[0]['generated_text'])
Build a command-line text summarizer using the efficient T5-small model.
textt5summarization
Create a tool that finds and replaces words with context-aware synonyms.
texttransformersnlp
Combine spaCy and transformers to extract important keywords from documents.
textspacykeywords
Build a zero-shot text classifier using the efficient DistilBERT model.
textdistilbertclassification
Create a tool to compare outputs from different AI models side by side.
textcomparisonanalysis
Develop a command-line tool to clean and preprocess text datasets.
textdatasetcleaning
Convert text to natural sounding speech using Bark or Coqui TTS systems.
audiottsspeechResources
-
# conda env create -f environment.yml
# conda activate tts-local
# conda deactivate
# conda env remove --name tts-local
name: tts-local
channels:
- defaults
- conda-forge
dependencies:
- python=3.10
- pytorch=2.3.0
- torchvision=0.18.0
- torchaudio=2.3.0
- pip
- pip:
- TTS
# GPU ADDITIONS
# Check cuda/gpu details using 'nvidia-smi'
# pip uninstall torch torchvision torchaudio -y
# pip install torch==2.3.0 torchvision==0.18.0 torchaudio==2.3.0 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121 --force-reinstall
# pip uninstall numpy
# pip install numpy==1.23.5
# python -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__)"
-
######### PART 1
if False:
from TTS.api import TTS
tts = TTS(model_name="tts_models/en/ljspeech/tacotron2-DDC", progress_bar=False)
tts.tts_to_file(text="This is a test of your local text-to-speech system.", file_path="test.wav", lang='en')
###### PART 2
import os
import torch
from TTS.api import TTS
# Sample text to synthesize
text = "This is a test of your local text-to-speech system."
# List of models to test
models = [
"tts_models/en/ljspeech/tacotron2-DDC",
"tts_models/en/jenny/jenny",
]
# Loop through test models and generate speech
for model_name in models:
try:
print(f"Synthesizing with model: {model_name}")
tts = TTS(model_name=model_name, progress_bar=False)
filename = model_name.split("/")[-1] + "_test.wav"
# Handle multi-speaker models
tts.tts_to_file(
text=text,
lang="en",
file_path=filename
)
print(f"Saved as: {filename}\n")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed with model {model_name}: {e}\n")
-
# Extra installs for bark:
# pip install git+https://github.com/suno-ai/bark.git
# pip install numpy torch soundfile scipy
import torch
print(torch.__version__) # Should show '2.3.0+cu121'
print(torch.cuda.is_available()) # Should return True
print(torch.version.cuda) # Should show '12.1'
# Basic test version
if False:
from bark import generate_audio, preload_models
import soundfile as sf
preload_models()
text = "This is Bark speaking. Welcome to the world of generative speech!"
audio_array = generate_audio(text)
sf.write("bark.wav", audio_array, 22050)
# bark_speech_enhanced.py
from bark import generate_audio, preload_models
import soundfile as sf
import librosa
# Load Bark models
preload_models()
# Define expressive text prompt
# text = "[narration][female][calm] Welcome to the world of generative speech. Bark is a powerful tool that brings text to life. Let's explore its capabilities together."
# text = "[narration][female][excited] Welcome to the world of generative speech. Bark is a powerful tool that brings text to life. Let's explore its capabilities together."
text = "Welcome to the world of generative speech. Bark is a powerful tool that brings text to life. Let's explore its capabilities together."
# Generate audio using a specific speaker preset
audio_array = generate_audio(text, history_prompt="v2/en_speaker_4")
# Generate audio from text
audio_array = generate_audio(text)
# Wave raw audio
sf.write("bark_raw.wav", audio_array, 22050)
# Load and normalize audio for improved clarity
y, sr = librosa.load("bark_raw.wav", sr=22050)
y = librosa.util.normalize(y)
# Wave enhanced audio
sf.write("bark_enhanced.wav", y, sr)
print("Speech generated and saved as 'bark_enhanced.wav'")
-
💡
bark.wav (Download WAV)
(419.42 KB)
-
💡
bark_enhanced.wav (Download WAV)
(666.92 KB)
-
💡
bark_raw.wav (Download WAV)
(570.04 KB)
-
💡
jenny_test.wav (Download WAV)
(298.57 KB)
-
💡
tacotron2-DDC_test.wav (Download WAV)
(3.09 MB)
-
💡
test.wav (Download WAV)
(169.07 KB)
Use Demucs to remove background noise and enhance audio quality.
audiodenoisingcleanup
Create an offline audio transcription tool using OpenAI's Whisper model.
audiowhispertranscription
Automatically generate and embed subtitles in videos using Whisper and FFmpeg.
audiosubtitlesvideo
Synthesize singing voices from text input using VITS and RVC technologies.
audiosingingvoice
Generate images from text prompts using Stable Diffusion optimized for low VRAM GPUs.
imagestable-diffusiongenerationResources
-
# conda env create -f environment.yml
# conda activate sd-lowvram
# conda deactivate
# conda env remove --name sd-lowvram
name: sd-lowvram
channels:
- pytorch
- conda-forge
- defaults
dependencies:
- python=3.10
- pip
- pytorch=2.3.0
- torchvision
- torchaudio
- pip:
- diffusers==0.27.2
- transformers==4.41.0
- accelerate==0.30.1
- safetensors==0.4.3
- Pillow>=10.0.0
- matplotlib>=3.7.0
- huggingface-hub==0.25.2
# GPU ADDITIONS
# Check cuda/gpu details using 'nvidia-smi'
# pip uninstall torch torchvision torchaudio -y
# pip install torch==2.3.0 torchvision==0.18.0 torchaudio==2.3.0 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121 --force-reinstall
# pip uninstall numpy
# pip install numpy==1.23.5
# python -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__)"
# GPU OPTIONAL MEMORY OPTIMIZER USING XFORMERS
# pip uninstall xformers -y --no-cache-dir
# pip install xformers==0.0.26.post1 --no-deps # the '--no-deps' stops it messing with the pytorch version
# python -c "import xformers; print(xformers.__version__)"
-
import torch
print(torch.__version__) # Should show '2.3.0+cu121'
print(torch.cuda.is_available()) # Should return True
print(torch.version.cuda) # Should show '12.1'
import torch
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline
# One-line device detection with CUDA version check
device = "cuda" if all([
torch.cuda.is_available(), # GPU exists
f"cu{torch.version.cuda.replace('.','')}" in torch.__version__ # Version matches (e.g., cu121)
]) else "cpu"
print(f"Using device: {device}")
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
torch_dtype=torch.float16 if device == "cuda" else torch.float32,
variant="fp16" if device == "cuda" else None,
# attn_implementation="sdpa", # Flash attention
# use_safetensors=True
safety_checker=None # Optional: disable safety checker for faster inference
).to(device)
if device == "cuda":
pipe.enable_attention_slicing()
try:
pipe.enable_xformers_memory_efficient_attention() # needs xformers
except:
print("xFormers not available, using default attention")
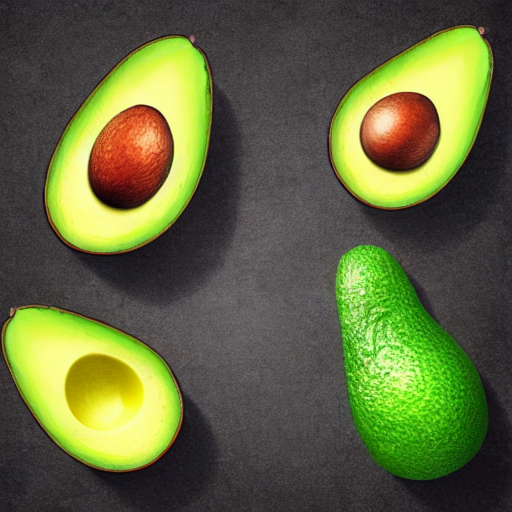
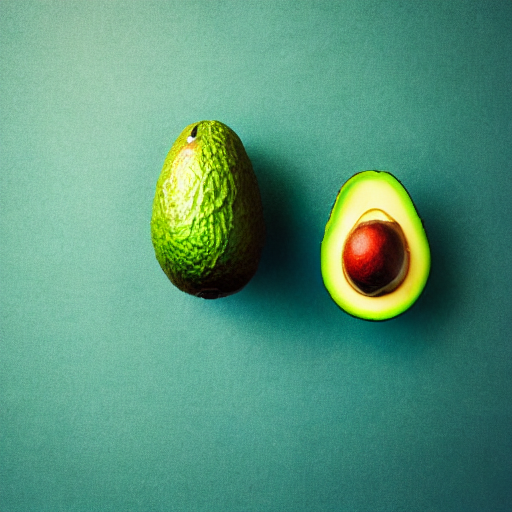
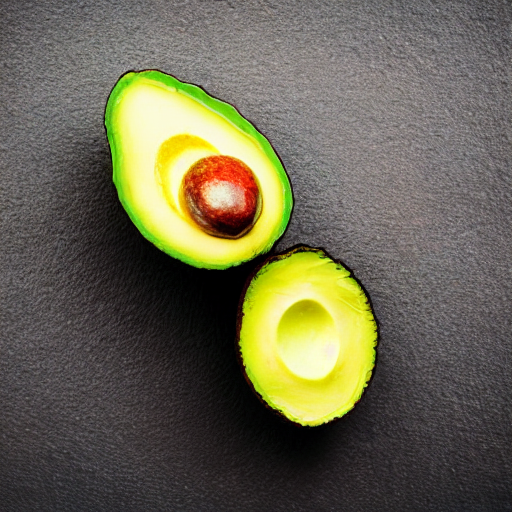
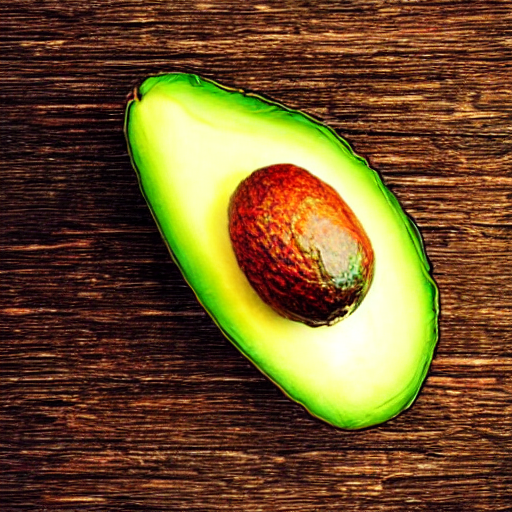
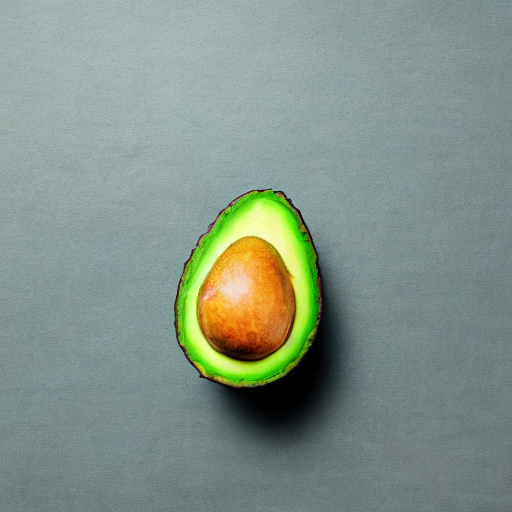
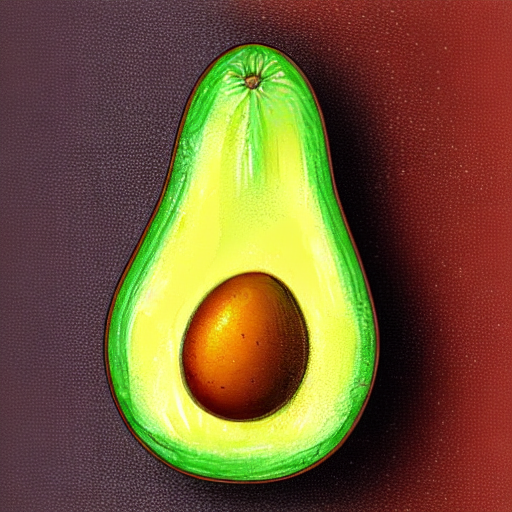
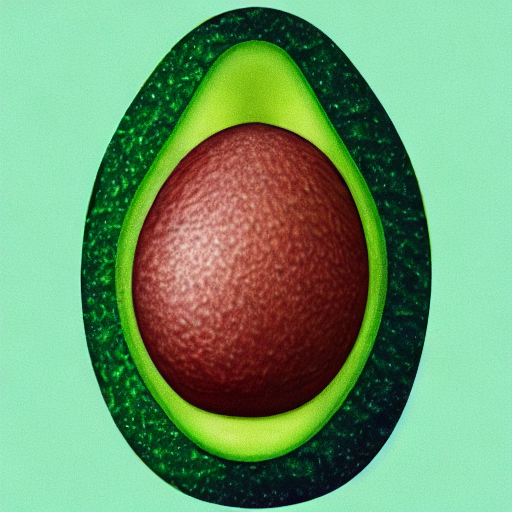
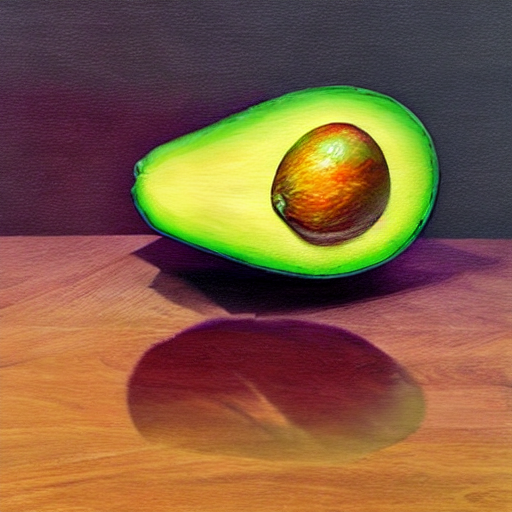
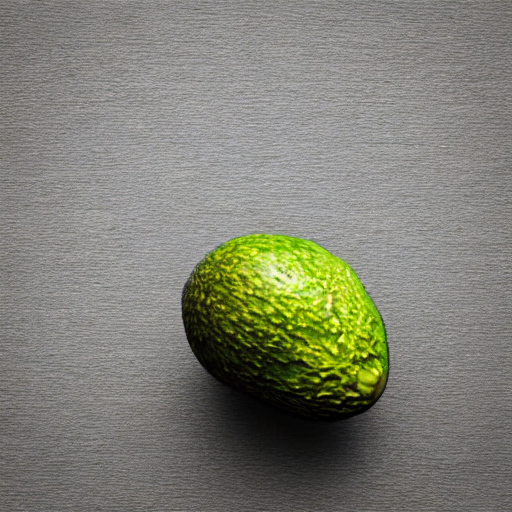
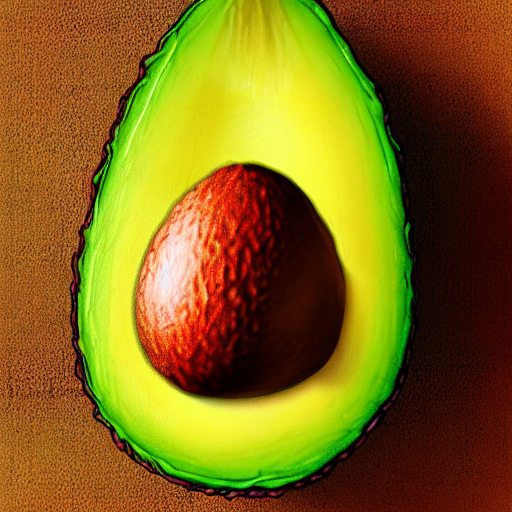
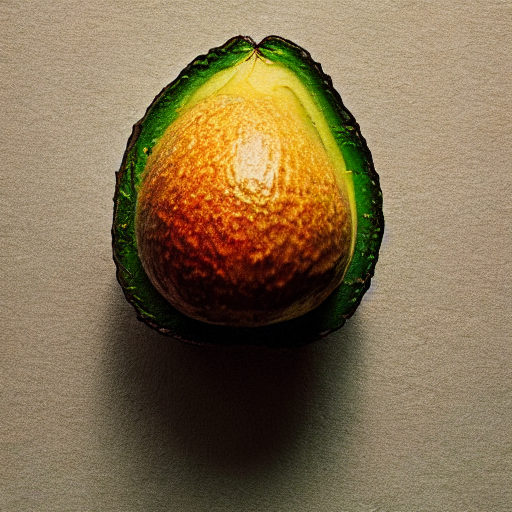
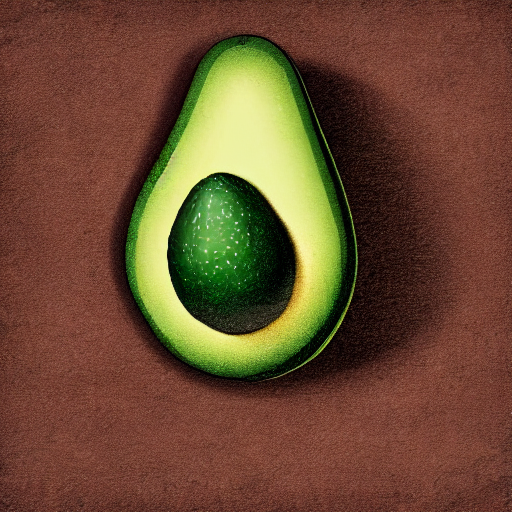
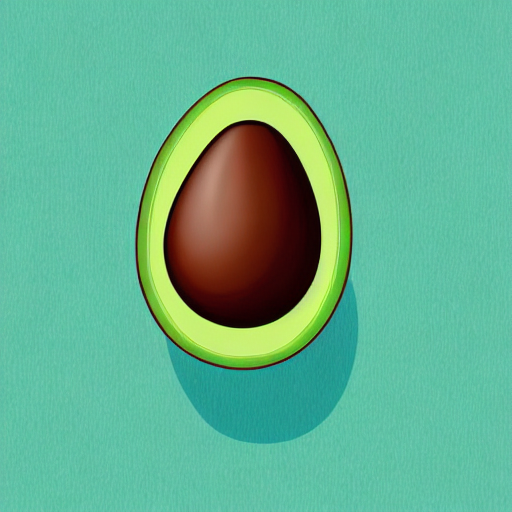
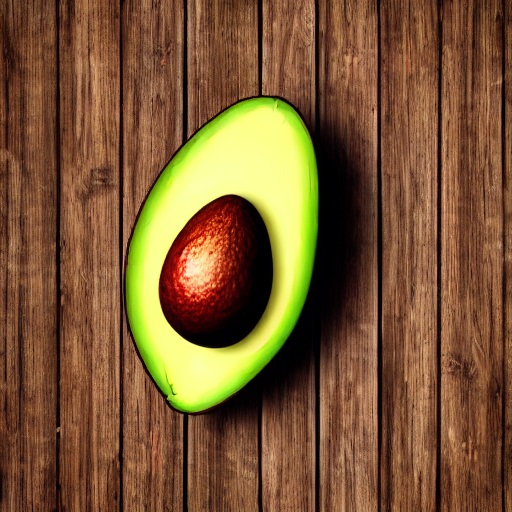
prompt = "an avocado on blank background, vivid colors, photorealistic"
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
image.save("output.png")
for i in range(0, 40):
image = pipe(prompt).images[0]
image.save(f"output_{i}.png")
'''
import torch
seed = 12345 # Pick any number
generator = torch.Generator(device=device).manual_seed(seed)
image = pipe(
prompt, # Text description of the desired image
height=512, # Output image height in pixels
width=512, # Output image width in pixels
num_inference_steps=50, # Denoising steps — higher means better quality
guidance_scale=7.5, # How closely to follow the prompt
negative_prompt="low quality, blurry", # What to avoid in the image
generator=generator, # Torch generator with manual_seed for reproducibility
output_type="pil", # Return type: PIL image (or numpy array)
callback=None # Optional function to monitor progress
).images[0]
'''
-
import torch
print(torch.__version__) # Should show '2.3.0+cu121'
print(torch.cuda.is_available()) # Should return True
print(torch.version.cuda) # Should show '12.1' or '11.8'...




















Create automatic image captions using the BLIP-2 vision-language model.
imagecaptioningblip
Turn text prompts into custom sticker designs using AI image generation.
imagestickersgeneration
Automatically generate descriptive tags for images using CLIP model.
imagetagsclip
Create detailed descriptions of images using the MiniGPT-4 model.
imagedescriptionminigpt
Produce artistic images from text prompts using VQGAN+CLIP combination.
imageartvqgan
Automatically generate memes by combining images with AI-generated captions.
imagememesgeneration
Convert text prompts into ASCII art representations using AI models.
imageasciiart
Create pictures composed of emojis based on text descriptions.
imageemojiart
Remove objects or fill missing parts of images using text-guided inpainting.
imageinpaintingstable-diffusionResources
-
# conda env create -f environment.yml
# conda activate sd-inpaint
# conda deactivate
# conda env remove --name sd-inpaint
name: sd-inpaint
channels:
- pytorch
- conda-forge
- defaults
dependencies:
- python=3.10
- pytorch=2.3.0
- torchvision
- torchaudio
- pip
- pip:
- diffusers==0.27.2
- transformers==4.41.0
- accelerate==0.30.1
- safetensors==0.4.3
- pillow>=10.0.0
- matplotlib>=3.7.0
- huggingface-hub==0.25.2
# GPU ADDITIONS
# Check cuda/gpu details using 'nvidia-smi'
# pip uninstall torch torchvision torchaudio -y
# pip install torch==2.3.0 torchvision==0.18.0 torchaudio==2.3.0 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121 --force-reinstall
# pip uninstall numpy
# pip install numpy==1.23.5
# python -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__)"
# GPU OPTIONAL MEMORY OPTIMIZER USING XFORMERS
# pip uninstall xformers -y --no-cache-dir
# pip install xformers==0.0.26.post1 --no-deps # the '--no-deps' stops it messing with the pytorch version
# python -c "import xformers; print(xformers.__version__)"
-
import torch
print(torch.__version__) # Should show '2.3.0+cu121'
print(torch.cuda.is_available()) # Should return True
print(torch.version.cuda) # Should show '12.1'
from PIL import Image
import torch
# One-line device detection with CUDA version check
device = "cuda" if all([
torch.cuda.is_available(), # GPU exists
f"cu{torch.version.cuda.replace('.','')}" in torch.__version__ # Version matches (e.g., cu121)
]) else "cpu"
print(f"Using device: {device}")
# Load pipeline
from diffusers import StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline
pipe = StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline.from_pretrained(
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting",
torch_dtype=torch.float16 if device == "cuda" else torch.float32,
variant="fp16" if device == "cuda" else None,
safety_checker=None, # Optional: disable safety checker for faster inference
).to( device )
'''
from diffusers import StableDiffusionXLInpaintPipeline
pipe = StableDiffusionXLInpaintPipeline.from_pretrained(
"diffusers/stable-diffusion-xl-1.0-inpainting-0.1",
torch_dtype=torch.float16 if device == "cuda" else torch.float32,
variant="fp16" if device == "cuda" else None,
safety_checker=None, # Optional: disable safety checker for faster inference
added_cond_kwargs={} # 👈 prevents the NoneType error
).to(device)
'''
# Load input image and mask
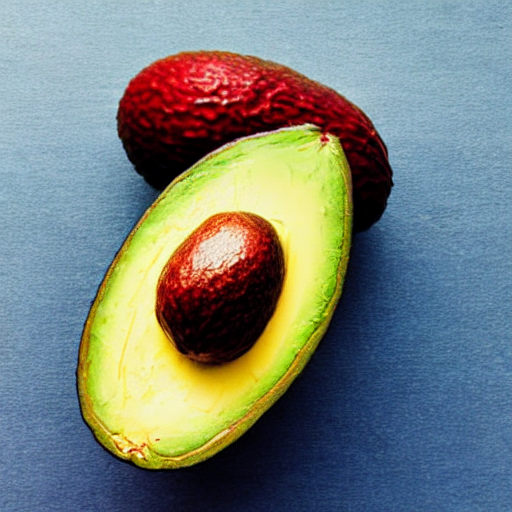
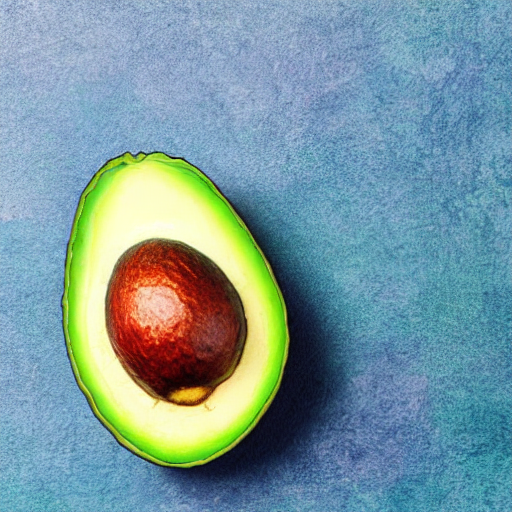
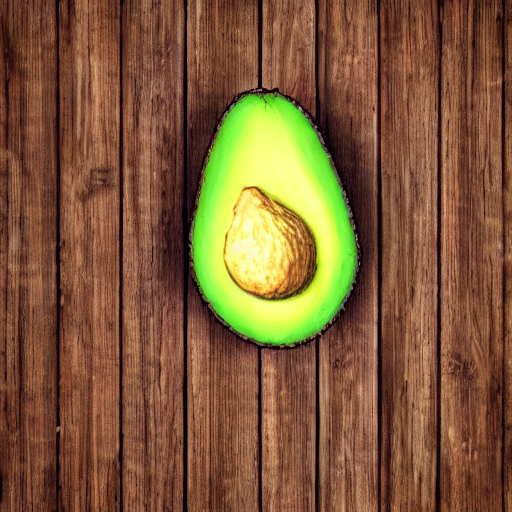
image = Image.open("avacado.jpg").convert("RGB").resize((512, 512))
mask = Image.open("mask.png").convert("L").resize((512, 512))
mask = mask.point(lambda p: 255 if p > 127 else 0) # binarize
# image = PIL.Image.open("avacado.jpg").convert("RGB")
# mask = PIL.Image.open("mask.png").convert("RGB")
# Inverse mask
# mask = Image.eval(mask, lambda x: 255 - x)
# Prompt
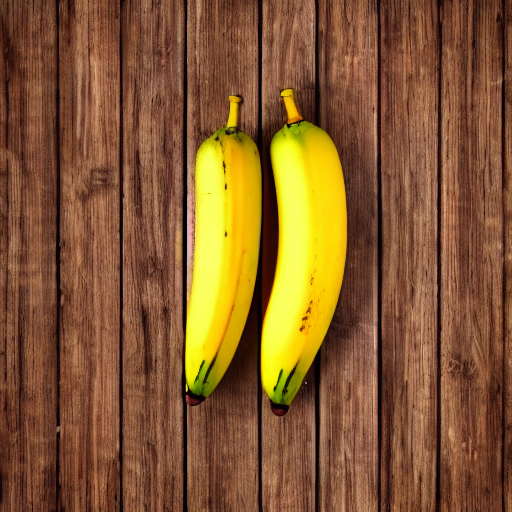
prompt = "Replace object with a ripe yellow banana, photorealistic"
# prompt = "clean background, seamless texture, no objects, empty space"
negative_prompt = "avocado, green, seed, oblong, deformed"
# Run inpainting
with torch.inference_mode():
result = pipe(prompt=prompt,
# negative_prompt=negative_prompt,
image=image,
mask_image=mask,
num_inference_steps=50, # Try 50-100 if needed
strength=1.0, # Forces full replacement
guidance_scale=9.0, # Stronger prompt adherence
).images[0]
result.save("result.png")




Enhance image resolution and quality using Real-ESRGAN model.
imageupscalingsuper-resolutionResources
-
# conda env create -f environment.yml
# conda activate real-esrgan
# conda deactivate
# conda env remove --name real-esrgan
name: real-esrgan
channels:
- pytorch
- conda-forge
- defaults
dependencies:
- python=3.10
- pytorch=2.0.1 # Officially paired with torchvision 0.15.2
- torchvision=0.15.2
- opencv # for image handling
- pip
- pip:
- requests
- pillow>=10.0.0
- tqdm
- numpy==1.23.5
- git+https://github.com/xinntao/Real-ESRGAN.git
- git+https://github.com/xinntao/BasicSR.git
# Or if you want to them with 'pip'
# pip install git+https://github.com/xinntao/Real-ESRGAN.git
# pip install git+https://github.com/xinntao/BasicSR.git
# GPU ADDITIONS
# Check cuda/gpu details using 'nvidia-smi'
# pip uninstall torch torchvision -y
# pip install torch==2.0.1 torchvision==0.15.2 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118 --force-reinstall
# python -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__)"
-
import torch
# Example output on your system:
print(torch.__version__) # "2.0.1+cu118"
print(torch.version.cuda) # "11.8"
print(torch.cuda.is_available()) # True
# Get device check
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() and f"cu{torch.version.cuda.replace('.','')}" in torch.__version__ else "cpu"
print(f"Using device: {device}")
import cv2
import os
import requests
from tqdm import tqdm
from basicsr.archs.rrdbnet_arch import RRDBNet
from realesrgan import RealESRGANer
def download_file(url, destination):
"""Download a file with progress bar"""
response = requests.get(url, stream=True)
total_size = int(response.headers.get('content-length', 0))
with open(destination, 'wb') as f:
with tqdm(total=total_size, unit='B', unit_scale=True, desc=f"Downloading {os.path.basename(destination)}") as pbar:
for data in response.iter_content(chunk_size=1024):
f.write(data)
pbar.update(len(data))
# Configuration
input_path = "input.jpg"
output_path = "output_upscaled.jpg"
model_dir = "weights"
model_name = "RealESRGAN_x4plus.pth"
model_url = "https://github.com/xinntao/Real-ESRGAN/releases/download/v0.1.0/RealESRGAN_x4plus.pth"
# Create weights directory if needed
os.makedirs(model_dir, exist_ok=True)
model_path = os.path.join(model_dir, model_name)
# Download weights if missing
if not os.path.exists(model_path):
print(f"Weights not found at {model_path}")
try:
download_file(model_url, model_path)
print("Download completed successfully!")
except Exception as e:
raise RuntimeError(f"Failed to download weights: {e}")
# Initialize model
model = RRDBNet(
num_in_ch=3,
num_out_ch=3,
num_feat=64,
num_block=23,
num_grow_ch=32,
scale=4
)
# Create upscaler
upsampler = RealESRGANer(
scale=4,
model_path=model_path,
model=model,
device=device,
tile=400, # Helps with large images - Tile size 0 for no tiling
tile_pad=10,
pre_pad=0,
half=False # Don't use half precision
)
# Single file
if False:
# Read input image
if not os.path.exists(input_path):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"Input image not found at {input_path}")
img = cv2.imread(input_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
if img is None:
raise ValueError(f"Failed to read image at {input_path}")
# Process image
try:
print("Upscaling image...")
output, _ = upsampler.enhance(img, outscale=4)
except Exception as e:
raise RuntimeError(f"Error during upscaling: {e}")
# Save output
cv2.imwrite(output_path, output)
print(f"Success! Output saved to {output_path}")
# Multiple files
if True:
scale=4 # 4x upscaling
input_folder = "images"
output_folder = "upscaled"
os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True)
for filename in os.listdir(input_folder):
if filename.lower().endswith(".jpg"):
img_path = os.path.join(input_folder, filename)
img = cv2.imread(img_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
if img is None:
print(f"Couldn't read {filename}, skipping")
continue
output, _ = upsampler.enhance(img, outscale=scale)
output_path = os.path.join(output_folder, filename)
cv2.imwrite(output_path, output)
print(f"\nDone! Upscaled images")
-
import torch
# Example output on your system:
print(torch.__version__) # "2.0.1+cu118"
print(torch.version.cuda) # "11.8"
print(torch.cuda.is_available()) # True
# Get device check
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() and f"cu{torch.version.cuda.replace('.','')}" in torch.__version__ else "cpu"
print(f"Using device: {device}")
import cv2
import os
import requests
from tqdm import tqdm
from basicsr.archs.rrdbnet_arch import RRDBNet
from realesrgan import RealESRGANer
def download_file(url, destination):
"""Download a file with progress bar"""
response = requests.get(url, stream=True)
total_size = int(response.headers.get('content-length', 0))
with open(destination, 'wb') as f:
with tqdm(total=total_size, unit='B', unit_scale=True, desc=f"Downloading {os.path.basename(destination)}") as pbar:
for data in response.iter_content(chunk_size=1024):
f.write(data)
pbar.update(len(data))
# Configuration
input_path = "input.jpg"
output_path = "output_upscaled.jpg"
model_dir = "weights"
model_name = "RealESRGAN_x4plus.pth"
model_url = "https://github.com/xinntao/Real-ESRGAN/releases/download/v0.1.0/RealESRGAN_x4plus.pth"
# Create weights directory if needed
os.makedirs(model_dir, exist_ok=True)
model_path = os.path.join(model_dir, model_name)
# Download weights if missing
if not os.path.exists(model_path):
print(f"Weights not found at {model_path}")
try:
download_file(model_url, model_path)
print("Download completed successfully!")
except Exception as e:
raise RuntimeError(f"Failed to download weights: {e}")
# Initialize model
model = RRDBNet(
num_in_ch=3,
num_out_ch=3,
num_feat=64,
num_block=23,
num_grow_ch=32,
scale=4
)
# Create upscaler
upsampler = RealESRGANer(
scale=4,
model_path=model_path,
model=model,
device=device,
tile=0, # Tile size (0 for no tiling)
tile_pad=10,
pre_pad=0,
half=False # Don't use half precision
)
# Read input image
if not os.path.exists(input_path):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"Input image not found at {input_path}")
img = cv2.imread(input_path, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
if img is None:
raise ValueError(f"Failed to read image at {input_path}")
# Process image
try:
print("Upscaling image...")
output, _ = upsampler.enhance(img, outscale=4)
except Exception as e:
raise RuntimeError(f"Error during upscaling: {e}")
# Save output
cv2.imwrite(output_path, output)
print(f"Success! Output saved to {output_path}")
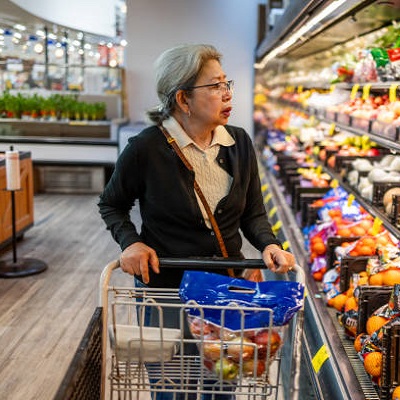
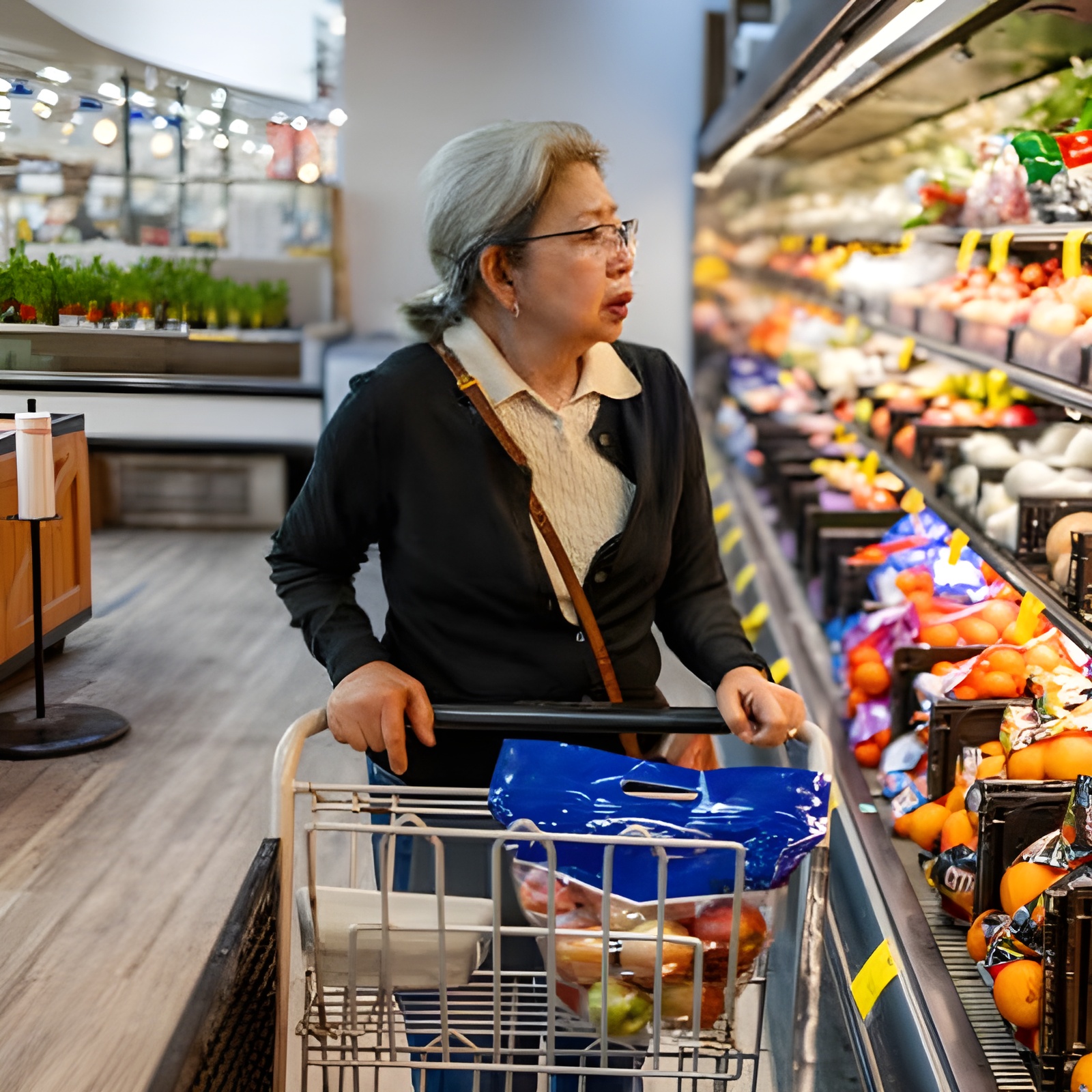


Generate multiple variations of an input image using diffusion models.
imagevariationsdiffusionResources
-
# conda env create -f environment.yml
# conda activate sd-img2img
# conda deactivate
# conda env remove --name sd-img2img
name: sd-img2img
channels:
- pytorch
- conda-forge
- defaults
dependencies:
- python=3.10
- pytorch=2.3.0
- torchvision
- torchaudio
- pip
- pip:
- diffusers==0.27.2
- transformers==4.41.0
- accelerate==0.30.1
- safetensors==0.4.3
- pillow>=10.0.0
- matplotlib>=3.7.0
- huggingface-hub==0.25.2
# GPU ADDITIONS
# Check cuda/gpu details using 'nvidia-smi'
# pip uninstall torch torchvision torchaudio -y
# pip install torch==2.3.0 torchvision==0.18.0 torchaudio==2.3.0 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121 --force-reinstall
# pip uninstall numpy
# pip install numpy==1.23.5
# python -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__)"
# GPU OPTIONAL MEMORY OPTIMIZER USING XFORMERS
# pip uninstall xformers -y --no-cache-dir
# pip install xformers==0.0.26.post1 --no-deps # the '--no-deps' stops it messing with the pytorch version
# python -c "import xformers; print(xformers.__version__)"
-
import torch
print(torch.__version__) # Should show '2.3.0+cu121'
print(torch.cuda.is_available()) # Should return True
print(torch.version.cuda) # Should show '12.1'
# Check device cpu or gpu
device = "cuda" if all([
torch.cuda.is_available(), # GPU exists
f"cu{torch.version.cuda.replace('.','')}" in torch.__version__ # Version matches (e.g., cu121)
]) else "cpu"
print(f"Using device: {device}")
from diffusers import StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline
from PIL import Image
import torch
# Load the model
pipe = StableDiffusionImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
torch_dtype=torch.float16 if device == "cuda" else torch.float32,
variant="fp16" if device == "cuda" else None,
safety_checker=None, # Optional: disable safety checker for faster inference
).to( device )
# Load input image
init_image = Image.open("input.jpg").convert("RGB")
init_image = init_image.resize((512, 512)) # required
# Prompt is optional!
# prompt = "make it look like a watercolor painting"
prompt = "make it look like a robot digital future picture"
# Generate variations
#images = pipe(prompt=prompt, image=init_image, strength=0.7, guidance_scale=7.5, num_inference_steps=50).images
images = pipe(
prompt=prompt, # Text prompt for generation
image=init_image, # Input image to transform
strength=0.8, # How much to alter the image (0=min change, 1=max change)
guidance_scale=11.5, # How closely to follow prompt (higher = more adherence)
num_inference_steps=50, # More steps = better quality but slower
negative_prompt="blurry, ugly", # What to exclude from output
num_images_per_prompt=1, # Number of variations to generate
eta=0.3, # DDIM randomness (0=deterministic, 1=random)
).images
# Save the result
for i, img in enumerate(images):
img.save(f"variation_{i+1}.png")




Extend images beyond their original boundaries using AI outpainting.
imageoutpaintingexpansionResources
-
# conda env create -f environment.yml
# conda activate sd-outpaint
# conda deactivate
# conda env remove --name sd-outpaint
name: sd-outpaint
channels:
- pytorch
- conda-forge
- defaults
dependencies:
- python=3.10
- pytorch=2.3.0
- torchvision
- torchaudio
- pip
- pip:
- diffusers==0.27.2
- transformers==4.41.0
- accelerate==0.30.1
- safetensors==0.4.3
- pillow>=10.0.0
- matplotlib>=3.7.0
- opencv-python>=4.8.0
- huggingface-hub==0.25.2
# GPU ADDITIONS
# Check cuda/gpu details using 'nvidia-smi'
# pip uninstall torch torchvision torchaudio -y
# pip install torch==2.3.0 torchvision==0.18.0 torchaudio==2.3.0 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121 --force-reinstall
# pip uninstall numpy
# pip install numpy==1.23.5
# python -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__)"
# GPU OPTIONAL MEMORY OPTIMIZER USING XFORMERS
# pip uninstall xformers -y --no-cache-dir
# pip install xformers==0.0.26.post1 --no-deps # the '--no-deps' stops it messing with the pytorch version
# python -c "import xformers; print(xformers.__version__)"
-
import torch
print(torch.__version__) # Should show '2.3.0+cu121'
print(torch.cuda.is_available()) # Should return True
print(torch.version.cuda) # Should show '12.1'
from PIL import Image
import torch
# One-line device detection with CUDA version check
device = "cuda" if all([
torch.cuda.is_available(), # GPU exists
f"cu{torch.version.cuda.replace('.','')}" in torch.__version__ # Version matches (e.g., cu121)
]) else "cpu"
print(f"Using device: {device}")
from diffusers import StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline
# Load image
image = Image.open("input.jpg").convert("RGB")
width, height = image.size
# Expand canvas and create mask
new_width = width + 512
new_height = height;
canvas = Image.new("RGB", (new_width, height), (255, 255, 255))
canvas.paste(image, (0, 0))
mask = Image.new("L", (new_width, height), 0)
for x in range(width, new_width):
for y in range(height):
mask.putpixel((x, y), 255)
# Load pipeline
pipe = StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline.from_pretrained(
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting",
torch_dtype=torch.float16 if device == "cuda" else torch.float32,
variant="fp16" if device == "cuda" else None,
safety_checker=None, # Optional: disable safety checker for faster inference
).to( device )
# Generate
# prompt = "a mountain landscape continuing to the right"
prompt = "trees"
result = pipe(prompt=prompt,
image=canvas,
mask_image=mask,
width=new_width, # Explicitly set output dimensions
height=new_height,
num_inference_steps=50, # Try 50-100 if needed
# strength=0.999, # Force for replacement
guidance_scale=9.0, # Stronger prompt adherence
).images[0]
result.save("outpainted_result.png")
-
import torch
print(torch.__version__) # Should show '2.3.0+cu121'
print(torch.cuda.is_available()) # Should return True
print(torch.version.cuda) # Should show '12.1'
from PIL import Image
import torch
# One-line device detection with CUDA version check
device = "cuda" if all([
torch.cuda.is_available(), # GPU exists
f"cu{torch.version.cuda.replace('.','')}" in torch.__version__ # Version matches (e.g., cu121)
]) else "cpu"
print(f"Using device: {device}")
from diffusers import StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline
import os
# Initialize
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
pipe = StableDiffusionInpaintPipeline.from_pretrained(
"runwayml/stable-diffusion-inpainting",
torch_dtype=torch.float16 if device == "cuda" else torch.float32,
safety_checker=None
).to(device)
# Parameters
num_outputs = 3 # Number of additional images to generate
prompt = "lush green trees, forest landscape, photorealistic, seamless continuation"
height = 512
step_size = 512 # Each output moves 512px right
# Load and prepare initial image
current_img = Image.open("input.jpg").convert("RGB").resize((512, height))
current_img.save("out0.jpg") # Save original as out0.jpg
for i in range(1, num_outputs + 1):
print(f"Generating out{i}.jpg...")
# Create canvas (512px wider than current image)
canvas = Image.new("RGB", (current_img.width + step_size, height), (0, 0, 0))
canvas.paste(current_img, (0, 0))
# Create mask (rightmost 512px)
mask = Image.new("L", canvas.size, 0)
mask.paste(255, (current_img.width, 0, canvas.width, height))
# Generate outpainted area
result = pipe(
prompt=prompt,
image=canvas,
mask_image=mask,
width=canvas.width,
height=height,
num_inference_steps=75,
guidance_scale=10.0,
).images[0]
# Crop to get just the new 512px portion
new_section = result.crop((current_img.width, 0, canvas.width, height))
new_section.save(f"out{i}.jpg")
# Update current image to the full outpainted result
current_img = result






Transform simple sketches into polished illustrations using AI.
imageenhancementdrawing
Convert line drawings into coloring book pages with AI assistance.
imagecoloringsketch
Implement face swapping between images using autoencoder architectures.
imagefaceswapautoencoder
Transform rough sketches into detailed artworks using ControlNet.
imagesketchcontrolnet
Create custom avatar images based on text descriptions.
imageavatargeneration
Build an image enhancement pipeline using SwinIR transformer model.
imagesuper-resolutionswinir
Adapt GPT-2 to your specific domain by fine-tuning on custom text data.
traininggpt-2fine-tuning
Customize T5 model for domain-specific text summarization tasks.
trainingt5summarization
Create an image captioning system trained on your personal photo collection.
trainingcaptioningcustom
Customize BERT for your specific text classification needs.
trainingbertclassification
Build a domain-specific tokenizer for your NLP projects.
trainingtokenizersentencepiece
Implement standard NLP evaluation metrics for model assessment.
trainingevaluationmetrics
Set up comprehensive training monitoring using W&B platform.
trainingmonitoringwandb
Learn to build and train a small transformer model from the ground up.
trainingtransformerscratch
Reduce model size and memory requirements through quantization.
trainingquantizationoptimization
Efficiently adapt large models using Low-Rank Adaptation technique.
trainingloraadapters
Set up and run LLaMA 2 language model on your local machine.
llmllamalocal
Deploy StableLM 3B model on standard consumer-grade hardware.
llmstablelmlocal
Optimize Mistral-7B to run efficiently on PCs with 16GB RAM.
llmmistraloptimization
Efficiently fine-tune LLaMA 2 using Quantized LoRA technique.
llmfinetuningqlora
Adapt StableLM model for specialized domains or applications.
llmfinetuningstablelm
Create a command-line interface chatbot using local LLMs.
llmchatbotcli
Implement retrieval-augmented generation with vector database integration.
llmragfaiss
Set up specialized coding LLMs for programming assistance.
llmcodinggeneration
Systematically evaluate different local LLMs on same prompts.
llmcomparisonevaluation
Build a system that routes queries to optimal LLM based on content.
llmrouterautomodel
Analyze performance differences between model sizes.
llmscalingcomparison
Learn to work with different model quantization formats.
llmformatsconversion
Practical guide to matching LLMs with available GPU resources.
llmhardwareselection
Create flexible command-line tool for loading various HF models.
llmhuggingfacecli
Measure and compare inference speed across different models.
llmbenchmarkperformance
Experiment with different tokenizers and prompt templates.
llmtokenizersprompting
Systematically evaluate different SD versions on same prompts.
imagestable-diffusioncomparisonResources
-
# conda env create -f environment.yml
# conda activate sd-compare
# conda deactivate
# conda env remove --name sd-compare
name: sd-compare
channels:
- pytorch
- conda-forge
- defaults
dependencies:
- python=3.10
- pip
- pytorch=2.3.0
- torchvision
- torchaudio
- pip:
- diffusers==0.27.2
- transformers==4.41.0
- accelerate==0.30.1
- safetensors==0.4.3
- Pillow>=10.0.0
- matplotlib>=3.7.0
- huggingface-hub==0.25.2
# GPU ADDITIONS
# Check cuda/gpu details using 'nvidia-smi'
# pip uninstall torch torchvision torchaudio -y
# pip install torch==2.3.0 torchvision==0.18.0 torchaudio==2.3.0 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121 --force-reinstall
# pip uninstall numpy
# pip install numpy==1.23.5
# python -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__)"
# GPU OPTIONAL MEMORY OPTIMIZER USING XFORMERS
# pip uninstall xformers -y --no-cache-dir
# pip install xformers==0.0.26.post1 --no-deps # the '--no-deps' stops it messing with the pytorch version
# python -c "import xformers; print(xformers.__version__)"
-
import torch
print(torch.__version__) # Should show '2.3.0+cu121'
print(torch.cuda.is_available()) # Should return True
print(torch.version.cuda) # Should show '12.1'
import torch
# One-line device detection with CUDA version check
device = "cuda" if all([
torch.cuda.is_available(), # GPU exists
f"cu{torch.version.cuda.replace('.','')}" in torch.__version__ # Version matches (e.g., cu121)
]) else "cpu"
print(f"Using device: {device}")
from diffusers import StableDiffusionPipeline, StableDiffusionXLPipeline
import torch
import gc
def load_model(model_name):
if "xl" in model_name.lower():
pipe = StableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0",
torch_dtype=torch.float16 if device == "cuda" else torch.float32,
variant="fp16" if device == "cuda" else None,
safety_checker=None
).to("cuda")
else:
pipe = StableDiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
model_name,
torch_dtype=torch.float16 if device == "cuda" else torch.float32,
variant="fp16" if device == "cuda" else None,
safety_checker=None
).to("cuda")
return pipe
# Your prompt
prompt = "A beautiful sunset over a mountain lake, digital art"
# Model list
models = {
"SD 1.5": "runwayml/stable-diffusion-v1-5",
"SD 2.1": "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1",
"SDXL": "stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0"
}
for name, model_id in models.items():
print(f"Generating with {name}...")
pipe = load_model(model_id)
# Generate the image
image = pipe(prompt=prompt, num_inference_steps=25, guidance_scale=7.5, width=512, height=512).images[0]
# Save the image
image.save(f"{name.replace(' ', '_').lower()}.png")
del pipe
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
gc.collect()






Benchmark different open-source text-to-image generation systems.
imagecomparisonmodels
Recommendations for optimal text2image models based on GPU memory.
imagehardwareoptimization
Fine-tune diffusers parameters for optimal performance.
imageoptimizationdiffusers
Compare different Stable Diffusion implementation approaches.
imageimplementationscomparison
Target specific components of diffusion models for efficient training.
imagefinetuningselective
Build a tool to automatically fetch and manage text2image models.
imagemodelsdownload
Bring still images to life with synchronized AI-generated voice.
imageanimationvoice
Automatically generate comic book pages from text scripts.
imagecomicsgeneration
Personalize text2image models with your own concepts or style.
imagedreamboothtraining
Create 3D objects from text descriptions using OpenDream.
3dgenerationopendreamResources
-
# conda env create -f environment.yml
# conda activate text-to-3d
# conda deactivate
# conda env remove --name text-to-3d
name: text-to-3d
channels:
- defaults
- conda-forge
- pytorch
dependencies:
- python=3.10
- pip
- pytorch=2.3.0
- torchvision=0.18.0
- pip:
- git+https://github.com/openai/shap-e.git
- tqdm
- numpy
- pyyaml
- ipywidgets
- numpy<2.0.0
# GPU ADDITIONS
# Check cuda/gpu details using 'nvidia-smi'
# pip uninstall torch torchvision torchaudio -y
# pip install torch==2.3.0 torchvision==0.18.0 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu121 --force-reinstall
# pip uninstall numpy
# pip install numpy==1.23.5
# python -c "import torch; print(torch.__version__)"
-
import torch
print(torch.__version__) # Should show '2.3.0+cu121'
print(torch.cuda.is_available()) # Should return True
print(torch.version.cuda) # Should show '12.1'
import torch
# Check device - cpu or gpu
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() and f"cu{torch.version.cuda.replace('.','')}" in torch.__version__ else "cpu"
print(f"Using device: {device}")
import torch
from shap_e.diffusion.sample import sample_latents
from shap_e.diffusion.gaussian_diffusion import diffusion_from_config
from shap_e.models.download import load_model, load_config
from shap_e.util.notebooks import decode_latent_mesh
prompt = "a shark"
xm = load_model('transmitter', device=device)
# Load model and diffusion process
model = load_model('text300M', device=device)
# diffusion = diffusion_from_config("shap_e/configs/diffusion/text300M.yaml")
diffusion = diffusion_from_config(load_config('diffusion'))
#import os
#config_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "shap-e", "shap_e", "configs", "diffusion", "text300M.yaml")
#diffusion = diffusion_from_config(config_path)
# Generate 3D latent
batch_size = 1
guidance_scale = 15.0
latents = sample_latents(
batch_size=batch_size,
model=model,
diffusion=diffusion,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
model_kwargs=dict(texts=[prompt] * batch_size),
progress=True,
clip_denoised=True,
use_fp16=True,
use_karras=True,
karras_steps=64,
sigma_min=1e-3,
sigma_max=160,
s_churn=0,
)
for i, latent in enumerate(latents):
t = decode_latent_mesh(xm, latent).tri_mesh()
with open(f'example_mesh_{i}.obj', 'w') as f:
t.write_obj(f)
with open(f'example_mesh_{i}.ply', 'wb') as f:
t.write_ply(f)
-
import torch
print(torch.__version__) # Should show '2.3.0+cu121'
print(torch.cuda.is_available()) # Should return True
print(torch.version.cuda) # Should show '12.1'
import torch
# Check device - cpu or gpu
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() and f"cu{torch.version.cuda.replace('.','')}" in torch.__version__ else "cpu"
print(f"Using device: {device}")
import torch
from shap_e.diffusion.sample import sample_latents
from shap_e.diffusion.gaussian_diffusion import diffusion_from_config
from shap_e.models.download import load_model, load_config
from shap_e.util.notebooks import decode_latent_mesh
prompt = "a cake with pink icing on the top"
xm = load_model('transmitter', device=device)
# Load model and diffusion process
model = load_model('text300M', device=device)
# diffusion = diffusion_from_config("shap_e/configs/diffusion/text300M.yaml")
diffusion = diffusion_from_config(load_config('diffusion'))
#import os
#config_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "shap-e", "shap_e", "configs", "diffusion", "text300M.yaml")
#diffusion = diffusion_from_config(config_path)
# Generate 3D latent
batch_size = 1
guidance_scale = 15.0
latents = sample_latents(
batch_size=batch_size,
model=model,
diffusion=diffusion,
guidance_scale=guidance_scale,
model_kwargs=dict(texts=[prompt] * batch_size),
progress=True,
clip_denoised=True,
use_fp16=True,
use_karras=True,
karras_steps=64,
sigma_min=1e-3,
sigma_max=160,
s_churn=0,
)
# Write .obj file with vertex colors
for i, latent in enumerate(latents):
# size is for the voxel resolution
mesh = decode_latent_mesh(xm, latent, size=384).tri_mesh()
vertices = mesh.verts
faces = mesh.faces
vertex_colors = mesh.vertex_channels.get("R", None)
with open(f'example_mesh_{i}.obj', 'w') as f:
# Write vertex positions and colors
for vi, v in enumerate(vertices):
# Default gray color if no color info
r, g, b = 0.5, 0.5, 0.5
if vertex_colors is not None:
r = mesh.vertex_channels["R"][vi]
g = mesh.vertex_channels["G"][vi]
b = mesh.vertex_channels["B"][vi]
f.write(f"v {v[0]} {v[1]} {v[2]} {r} {g} {b}\n")
# Write face indices (OBJ is 1-based)
for face in faces:
f.write(f"f {face[0]+1} {face[1]+1} {face[2]+1}\n")
print(f"Saved mesh with vertex colors to example_mesh_{i}.obj")
-
🔍
cake-with-icing.obj (Download OBJ)
(16.05 MB)
-
🔍
example_mesh_1.obj (Download OBJ)
(1.61 MB)
-
🔍
example_mesh_2.obj (Download OBJ)
(1.49 MB)
-
🔍
example_mesh_3.obj (Download OBJ)
(1.79 MB)
-
🔍
shark-vertex-colors.obj (Download OBJ)
(1.53 MB)
-
💡
example_mesh_0.ply (Download PLY)
(385.27 KB)
-
💡
example_mesh_1.ply (Download PLY)
(424.41 KB)
-
💡
example_mesh_2.ply (Download PLY)
(394.04 KB)
-
💡
example_mesh_3.ply (Download PLY)
(469.01 KB)
Apply artistic styles to images using diffusion techniques.
imagestyle-transferdiffusion
Generate smooth slow-motion videos using frame interpolation.
videointerpolationframes
Experiment with motion generation using LoRA adapters.
videolorageneration
Generate realistic faces using StyleGAN techniques.
imageganfaces
Create visual music videos automatically from song lyrics.
videomusicgeneration
Build a browser interface for Stable Diffusion using Gradio.
webgradioui
Create an end-to-end system that generates images from voice commands.
webvoicegeneration
Build a chatbot that understands both images and text inputs.
webchatbotmultimodal
Create a personalized assistant trained on your own documents.
webassistantcustom
Build a web app that generates customized travel itineraries.
webtravelplanning
Create a system that generates recipes from ingredient photos.
webrecipesocr
Build an interactive text adventure game powered by LLMs.
webgameinteractive
Create a tool that converts handwritten notes to formatted markdown.
webocrmarkdown
Build a web interface for summarizing uploaded PDF documents.
webpdfsummarization
Create a production-ready API endpoint for your AI model.
deploymentfastapiserving
Package your AI application in Docker for easy deployment.
deploymentdockercontainer
Optimize CUDA usage for better local model performance.
optimizationcudainference
Set up system monitoring for GPU-intensive AI applications.
optimizationvrammonitoring
Accelerate transformer models using ONNX runtime.
optimizationonnxspeed
Implement asynchronous processing for high-load model serving.
deploymentscalingqueue
Reduce model size for better local deployment options.
optimizationquantizationcompression
Set up a system that can serve different models simultaneously.
deploymentscalingconcurrent
Create and deploy an AI-powered Discord chatbot.
deploymentdiscordbot
Build a professional installer that checks system requirements.
deploymentcliinstaller
Implement tools to identify machine-generated text content.
ethicsdetectiontext
Add invisible watermarks to identify AI-generated visuals.
ethicswatermarkimages
Analyze model outputs for potential biases and stereotypes.
ethicsbiasdetection
Set up conversations between different AI language models.
creativedialoguesimulation
Build a system that generates humorous parodies of existing content.
creativeparodygeneration
Implement proper authentication for AI model APIs.
securityapiauthentication
 | Resources |  |
• Python Programming [LINK]
• Artificial Intellengence (AI) [LINK]
• Data Mining & Machine Learning [LINK]
|
|